| ID |
Date |
Author |
Type |
Category |
Subject |
|
29
|
Mon Feb 13 18:57:53 2023 |
Aiden | Summary | General | Clean and Bake batch 2 |
| Cleaned second batch of SS parts with liquinox for 20 min. Then put in oven for 5 steps; 1. Ramp, 100 degC, 15 min 2. Const, 100 degC, 30 min 3. Ramp, 200 degC, 30 min 4. Const, 200 degC, 48 hours 5. Ramp, 25 degC, (off). |
|
28
|
Sat Feb 11 17:09:29 2023 |
Shane | Update | General | clean room particle counts 2/10/23 |
| Took a round of clean room counts after the latest clean of vacuum chamber on Feb 10. Used 60 second sample time, 5 samples for each of the 5 zones. Plots attached for both occupied clean room (one person inside, attachment 1) and unoccupied clean room (empty attachment 2), as well as the raw data from the particle counter (attachment 3). |
| Attachment 1: occupied2.10.23.pdf
|

|
| Attachment 2: unoccupied2.10.23.pdf
|

|
| Attachment 3: particlecounts2.10.23.PDF
|

|
|
27
|
Sat Feb 11 00:17:27 2023 |
Julian | Update | General | Vacuum Chamber Cleaning |
| Today I finished wiping down the rest of the vacuum chamber, specifically focusing on the connecting ports and outside surface of the chamber. When I was finished, I test wiped every surface of the chamber and took pictures confirming the current state of cleanliness; Attachment 1 "Wipes for top and bottom of chamber's upper lip." Attachment 2 " Top and bottom of chamber's lower lip." Attachment 3 "Inside and Outside main chamber." Attachment 4 "Inside connecting ports." |
| Attachment 1: 20230210_181404.jpg
|

|
| Attachment 2: 20230210_181424.jpg
|

|
| Attachment 3: 20230210_181541.jpg
|

|
| Attachment 4: 20230210_181606.jpg
|

|
|
26
|
Fri Feb 10 16:34:45 2023 |
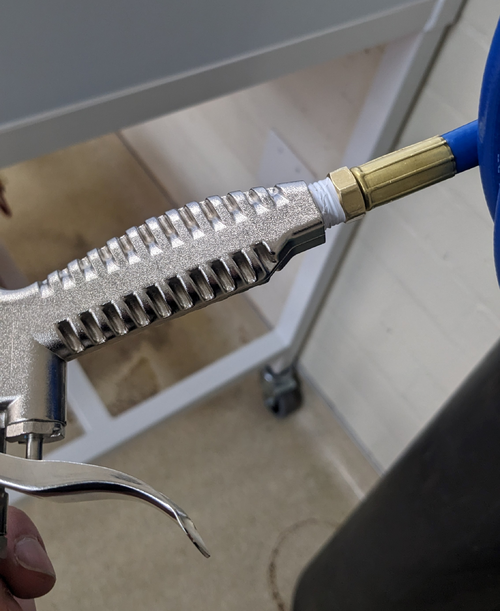
Huy Tuong Cao | Infrastructure | Clean & Bake | Nitrogen gas tank ready to use |
| Cao,
Today I fixed the final bit related to the nitrogen gas tank, which is to apply sealing tape to M-NPT connector of the hose to prevent
leakage (file: AirGunSealed.jpg)
After application of the tape, no audible leak can be heard from connection between the hose and the air gun.
The general operating procedure for the gas tank is as following:
- Turn the regulator (blue handle) anti-clockwise still it's loose
- Turn the valve on nitrogen as tank anti-clockwise, immediately the RHS meter of the regulator would jump to approx 2000 psi. This is the standard pressure for high pressure gas tank
- Turn the regulator clock-wise slowly until the pressure one the LHS meter face reads approx 60 psi. This is sufficient for drying parts with. At this point, the flow pressure still should register zero
- Press the trigger on the air gun, a high pressure air flow should come out and the flow meter should increase
- When finished, close the gas tank valve, turn the regulator anti-clockwise, then press the air gun trigger to release gas left in the hose/gun
|
| Attachment 1: AirGunSealed.jpg
|

|
|
25
|
Fri Feb 10 15:15:30 2023 |
Aiden | Update | General | Bagging First Batch |
| Aiden Bagged and Tagged the first batch of stainless steel parts shown on the google spread sheet.
1. Removed two parts from the oven.
2. Place them in the ESD bag.
3. Seal bag with Kapton Tape.
4. Create label including part name and number underneath it.
5. Put label onto the side of the bag where it is not sealed with tape.
6. Placed bagged items into clean room on work table.
ps. total bags in first batch = 4 |
|
24
|
Tue Feb 7 17:44:17 2023 |
Jon | Infrastructure | Computers | Workstation 1 (ws1) set up |
| The Linux workstation (ws1) that used to sit on the old workbench has been mounted on the new electronics bench and is now ready for use again. I upgraded the OS to Debian 11.6 and also upgraded the CDS workstation tools. |
| Attachment 1: ws1.jpg
|

|
|
23
|
Tue Feb 7 17:27:30 2023 |
Aiden | Physics | ELOG | Clean and Bake Batch #1 |
| Cleaned SS parts with liquinox for 20 min. Then put in oven for 5 steps;
1. Ramp, 100 degC, 15 min
2. Const, 100 degC, 30 min
3. Ramp, 200 degC, 30 min
4. Const, 200 degC, 48 hours
5. Ramp, 25 degC, (off)
PS. Ultrasonic washer does not have heating feature. |
|
22
|
Mon Feb 6 20:02:32 2023 |
Julian | Update | General | Cleanroom Update |
| I wiped down the main table (including frame, legs, and transparent shelf) and workbench using alcohol wipes. Once I cleaned all of the surfaces, I used the Hepa vacuum to pick up any fallen debris. |
|
21
|
Sat Feb 4 17:01:03 2023 |
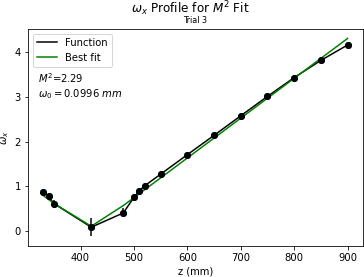
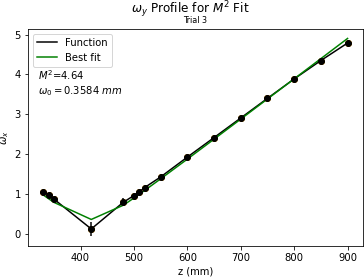
Peter | Update | VLC Electronics | Laser Data |
| Peter and Ryan took laser beam data. Configuration: 100mm focal length lens is ~100mm from lens. 150mm focal length lens is ~200mm from first lens. Beam waist is ~420mm from second lens.
Beam waist is very small still. Had to input large amounts of error in data collection. Took width data successively at points near waist and at >= Rayleigh range. Plots are shown below.
Key points:
Took a while to figure out optimum configuration for lenses to be placed so that an accessible beam waist could be obtained.
Beam waist is still very small. May need to do an ABCD calculation to see if there is anything bigger that can be obtained. |
| Attachment 1: OmegaX_M2_Fit_3.png
|
|
| Attachment 2: OmegaY_M2_Fit_3.png
|
|
|
19
|
Fri Feb 3 13:04:04 2023 |
shane | Summary | General | clean room particle counts 1/25/23 |
| Clean room count graphs for each zone (as of January 25, 2023) attached |
| Attachment 1: cleanroomcountsJan25.pdf
|

|
|
18
|
Fri Jan 27 18:44:31 2023 |
Julian | Update | General | Vacuum Chanmber Cleaning |
| I used the IPA wipes to wipe down the inside of the chamber the best I could. I cleaned the main chamber but not any of the connecting joints. When I finished I did a once over with a fresh wipe and found no residue. |
|
17
|
Thu Jan 26 18:58:25 2023 |
Aiden | Update | General | Oven Heating |
| Aiden cleaned the oven with methanol again and set the oven to 260 degC for 12 hours. |
|
16
|
Mon Jan 23 17:26:15 2023 |
Peter Carney | Update | General | Oven cleaning |
| Aiden and Cao
Turned on the oven to 120 deg C for 12 hours. After 12 hours, put it at 200 deg C for 48 hours. |
|
15
|
Wed Jan 18 22:06:05 2023 |
Julian | Update | ELOG | Cleanroom Update |
| I wiped down all the inner walls of the cleanroom using alcohol wipes, as per Cao's instruction. |
|
14
|
Wed Dec 14 18:34:33 2022 |
Jon | Configuration | Electronics | Adapter for 532 nm laser power supply |
| I installed an EU-to-US plug adapter for the 532nm laser's 9V power supply. I then re-measured the laser's power with the correct supply voltage (previously we had been using a 6V supply). At 9V, the max power is 0.83 W, so the laser is confirmed to be Class 2 as labeled. |
| Attachment 1: laser_power.png
|
|
|
13
|
Wed Dec 14 17:35:41 2022 |
Jon | Infrastructure | Computers | Windows Laptop |
I set up the new Windows 10 laptop (pictured below), which arrived yesterday. This laptop is intended to be used for running lightweight Windows-only programs, such as the Thorlabs beam profiler software or the SRS RGA client. However, none of that software is installed yet.
Configuration details
As usual, the computer is configured with one shared account (username: controls) and the standard password. Note that it is connected to the campus wifi (UCR-SECURE).
If a connection to the lab's local network is required, then the laptop must be connected by an Ethernet cable to the switch in the top of the server rack. |
| Attachment 1: laptop.png
|

|
|
12
|
Mon Nov 28 18:10:23 2022 |
shane | Update | ELOG | Particle counts in the clean room |
| Particle count stats for the clean room Nov 28, 2022:
Took 10 sample runs in each of 5 regions in the clean room (5 runs per region with a person inside the clean room for the measurement, and 5 runs per region without anyone in the clean room for the measurement), for a total of 50 samples taken. Sample time was 60 seconds. Overall clean room average particle count for the size ranges are as follows:
0.3 micrometers- 3405.76 (room occupied), 974.92 (room empty)
0.5 micrometers- 409.72 (room occupied), 409.72 (room empty)
1.0 micrometers- 1102.2 (room occupied), 282.6 (room empty)
2.5 micrometers- 692.32 (room occupied), 183.68 (room empty)
4.0 micrometers- 254.28 (room occupied), 84.72 (room empty)
5.0 micrometers- 141.24 (room occupied), 84.72 (room empty)
7.0 micrometers- 56.48 (room occupied), 84.72 (room empty)
10.0 micrometers- 42.36 (room occupied, 42.36 (room empty)
More statistics (including individual stats on the 5 regions within the clean room) attached. |
| Attachment 1: clean_room_particle_counts_11_28_-_Sheet1.pdf
|

|
|
11
|
Mon Oct 3 17:21:39 2022 |
Cao | Update | TCS | Inspection of macor parts |
The macor parts arrived and inspected today. These include:
- Macor spacer (drawing:
LIGO_Redesign_Macor_Spacer_Drawing_v4.pdf attached below), quantities: 40
- No defects, damages observed
- Parts are free from grease/ machining fluid
- Wall thickness of 1 mm appear to provide sufficient stiffness to part
- Images of parts:
Macor_spacer_0.jpg, Macor_spacer_1.jpg
- Macor 5-40 UNC screw (drawing:
LIGO_Redesign_Macor_Screw_Drawing_v6.pdf attached below), quantities: 20
- One screw broke, location of break: should edge between head and shaft (see image
Macor_screw_5.jpg )
- All other screws look ok, no damage observed, clean surface overall
- Images:
Macor_screw_0.jpg , Macor_screw_4.jpg
|
| Attachment 1: LIGO_Redesign_Macor_Spacer_Drawing_v4.pdf
|

|
| Attachment 2: Macor_spacer_0.jpg
|

|
| Attachment 3: Macor_spacer_1.jpg
|

|
| Attachment 4: LIGO_Redesign_Macor_Screw_Drawing_v6.pdf
|

|
| Attachment 5: Macor_screw_5.jpg
|

|
| Attachment 6: Macor_screw_0.jpg
|
|
| Attachment 7: Macor_screw_4.jpg
|

|
|
10
|
Wed Aug 17 16:04:30 2022 |
Phoebe Zyla | Summary | Lore | Testing the Cartridge Heater and Collecting FLIR Data |
We have tested the heater to find emissivity, mounted the heater system to the optical table, and have taken irradiance maps of the heater projected onto the screen.
The heater's emissivity was determined by using a thermocouple in conjunction with the FLIR's temperature calibration. To attach the thermocouple to the heater initially, I used Kapton tape and ran both the wires of the heater and the thermocouple through the heater bridge. This allowed for the heater to rest on an optical post and be observed without anyone directly holding it, but there were some measurement issues. The thermocouple had a very wide range of temperatures it was reading, which may have been due to intermittent contact or a short between the two legs of the thermocouple. To solve this and make the temperature measurements more stable, we pried apart the two ends of the thermocouple (to ensure there was no short) and put tape on either side, leaving the end connection bare. This was then taped to the heater, and the thermocouple was much more stable. We also used a K-type thermocouple that has an adhesive tape on it already, which assisted with the intermittent contact as well. With the thermocouple measuring the temperature of the heater, we could point the FLIR directly at the heater and calibrate the emissivity until the FLIR and the thermocouple agreed. Cassidy's emissivity calculator was also used, as I could input a temperature and observe what the emissivity of an area was based on that temperature. We found the emissivity of the heater to be 0.57.
As a note, when observing the heater with the FLIR, it appeared that there was a hot spot in the center, where the Kapton tape sat. Because the Kapton has a different emissivity than the 304 stainless steel of the heater, the FLIR will read it as having a different temperature than it actually does. When using the FLIR in the future, be sure to ascertain whether there is a temperature difference somewhere or if there may be different emissivities.
Additionally, the first heater that I used was taken to a very high temperature and oxidized. The emissivity of this oxidized heater is not known, but could be good information for knowing how oxidation affects these heaters specifically.
To mount the heater system in front of the screen, I used 1/2'' optical posts and the mount I designed using COMSOL's CAD program. The heater was originally 2.5 inches away from the screen, and has since been moved back by an additional two inches so that we could observe the heater side of the screen with the FLIR. We wanted to see what temperature the heater side of the screen was when irradiated by the heater, and how that compared to the camera side of the screen. When the heater ran at 1.12 W of input power, the heater side of the screen had a max temperature of around 29.7 C, and the camera side of the screen read at about 29.5 C. This means that there is very little thermal loss between the two sides of the screen, and any insulation that the screen's adhesive may have is largely negligible. Additionally, the camera was placed at an angle and undetermined distance for these tests, confirming that the temperature measurements compensate well/donít depend on changes in angle or distance between the camera and the screen. However, there was spots on the back of the screen that the camera was measuring as hot spots where there shouldnít have been any. I have included an example below. It would be useful to run a test where the camera is directly on the back of the screen without the heater to characterize the screen and see if the hot spots are physically present on the screen or if this is an artifice of the camera because of something like angle of viewing.
Taking irradiance maps of the screen was straightforward. After checking that the emissivity of the screen is 0.99 by viewing it at room temperature, we monitored the max temperature while slowing increasing the wattage the heater was running at. There is not a large change until the heater is at around 95 C, at which point the screen began to rise in temperature from 27 C to 28 C. We took measurements of this while the heater was 2.5 and 4.5 inches away from the screen. The irradiance map has a very symmetrical and circular shape, but does not have the ring pattern that we expected. There may be a few reasons for this: there could be some conduction between the two sides of the screen that is causing the pattern to spread further, the heater setup may not be as ideal as it was modeled to be, or there could be a different, unknown issue.
TO DO:
- It would be useful to run a test of the camera in multiple different positions to ensure our conclusion that the cameraís measurements donít depend on angle or distance (or that these factors are well accounted for in the current temperature calculations) is correct.
- Measure the back of the screen straight on to identify bright spots and possible reasons as to their appearance.
- Recalibrate camera to ensure it is still correct after testing in multiple positions.
- Take another irradiance map of the screen at a higher input power, as well as moving the heater close/further away to try and replicate the COMSOL irradiance maps. It would be useful to also redo the COMSOL modeling at lower powers and variable distances.
Pictures included of full table setup, the heater mount, the heater with Kapton tape attaching the thermocouple as well as FLIR's measured irradiance map. |
| Attachment 1: Screenshot_(74).png
|
.png.png)
|
| Attachment 2: Screenshot_(75).png
|
.png.png)
|
| Attachment 3: Screenshot_from_2022-08-15_11-24-40.png
|

|
| Attachment 4: AcquisitionImage(Aug-15-2022_14_16).jpg
|
.jpg.png)
|
|
9
|
Tue Jul 26 14:10:35 2022 |
Cassidy | Update | Cameras | Optical Post Replacement and Realignment |
| Today I replaced the 3" optical post that the camera rests on with a 2" optical post in order for the screen to correctly fill out the camera's FOV. The 3" post is now in the glass optics cabinet next to the FLIR camera configuration box, wrapped in the protective materials from the 2" post for safekeeping.
There were no issues with the physical replacement of the post, except that the fork clamp on the post needs to be on one of the perpendicular, not diagonal, axes in order to be secure. I chose the front axis (towards the screen) as before in order to easily access the alignment knobs.
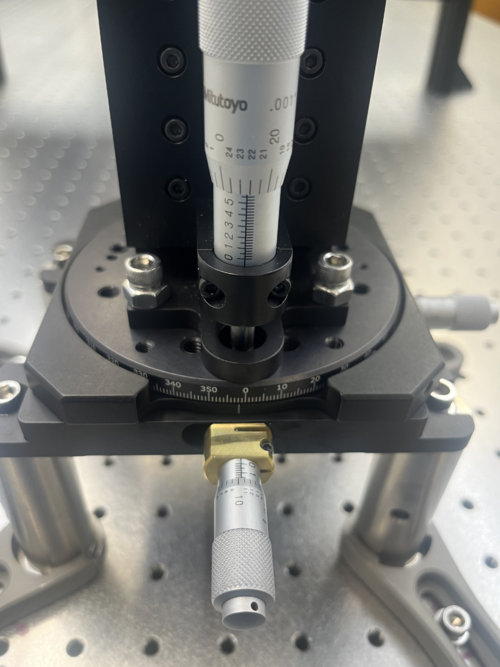
To align, I followed the same process as last time except for a more purposeful original rough alignment. For alignment purposes, the visual camera was used. For the first rough alignment, I pulled the camera as far back as possible on the x axis (with the z axis roughly centered), then moved the entire stage setup back until I could just see both the top and bottom edge of the screen. Then, I set the z-axis to an extreme in order to use the edge of the screen to align the rotational and y-axis pieces for the fine alignment.
For the fine alignment, starting with the z and x axis at extremes, I began by aligning the rotational axis. To do this, I used the gaps between the top of the screen and the camera window on the far left and right of the image. When these gaps were equal I knew the rotation was adequately set. Then, I set the y-axis so that the pattern was centered. If the gaps were no longer even, I redid the rotation alignment and ditto with the y axis until both were set. This resulted in a rotation of about two degrees and a y axis at just under 3.5.
To set the z and x axis, I centered the z-axis using the top and bottom of the screen, which should both be visible if the rough alignment was done correctly. Then, I adjusted the x axis by pushing it forward until the top and bottom of the screen were just out of the frame. As with the rotational and y-axis, I iteratively fine tuned the x and z axis until both the image was centered in the z axis and only the screen was in view. This resulted in a z-axis value of just over 5.5 and an x axis value of nearly 1.75.
Pictures are included of all alignment knobs and the new post/stage setup! |
| Attachment 1: YAxisAlignment.png
|

|
| Attachment 2: XRotZAlignment.png
|
|
| Attachment 3: NewOpticalPost.png
|
|
|
8
|
Fri Jul 22 13:20:28 2022 |
Phoebe | Update | | Comsol |
| I will be using comsol until 1:30 pm today. I will be updating the model for the heater mount to be thicker in certain areas, so that it can feasibly be 3D printed. Specifically, the radius of the center cartridge mount has been increased to add thickness to the pipe and the arms of the bridge. This will allow us to print with a much smaller chance for error, as the printer can print objects with a minimum length of 1 mm. |
|
7
|
Mon Jul 11 14:29:45 2022 |
Jon | Omnistructure | General | HEPA filter installed |
| Today I unpacked and installed the new HEPA filter for the lab. It is an Omni CleanAir OCA1210 capable of 1200 CFM. This flow rate is sufficient to turn over the air in the room once every 4 minutes, or 14 times per hour. Hopefully this will cut down on our particulate accumulation issues. |
| Attachment 1: IMG_1530.png
|

|
|
6
|
Tue Jun 21 18:31:49 2022 |
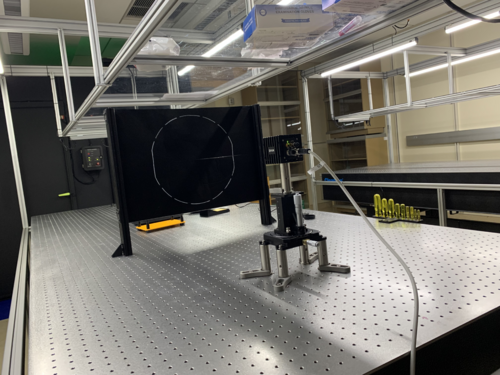
Cassidy and Phoebe | Update | Cameras | IR Absorbing Screen and FLIR Camera Setup |
Today we set up the IR absorbing screen and the camera on the optical table, as well as tested that the camera was functioning as expected (picking up heat sources beyond the screen).
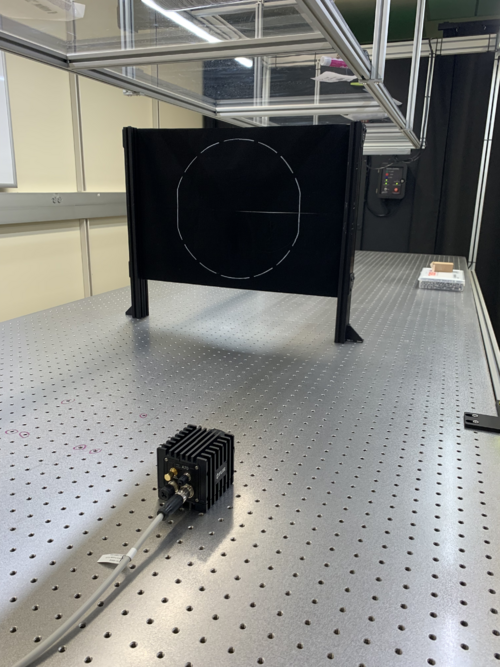
Screen Setup
The screen was set up by clamping it between two rectangular posts on each side. First, two posts were set up with 22 in. between them (thus allowing the screen to span a total distance of up to 24 in. when clamped down). To best stabilize the screen and to allow for it to be "pulled" taut by exploiting the give in the L-bracket, the L-bracket was bolted on the outside of the post, along the same axis as the screen itself.
On first attempt, the screen was too thin to be fully clamped between the posts. In order to have it fit snugly, sections of heat shrink tubing was used as a shim at the points where the posts were clamped together. The tubing was slid into the track of one optical post at the desired points. In order to accommodate the shim, the two posts had to be held together, ideally clamped, with the screen and shim in place. Then, the post clamps could be slid into the tracks of the post, moved to the optimal location, and tightened down. This required at least three people: two to tighten one side while the third holds up the screen on the other side. The screen was placed ~1/8" from the edge of the posts and flush with the top.
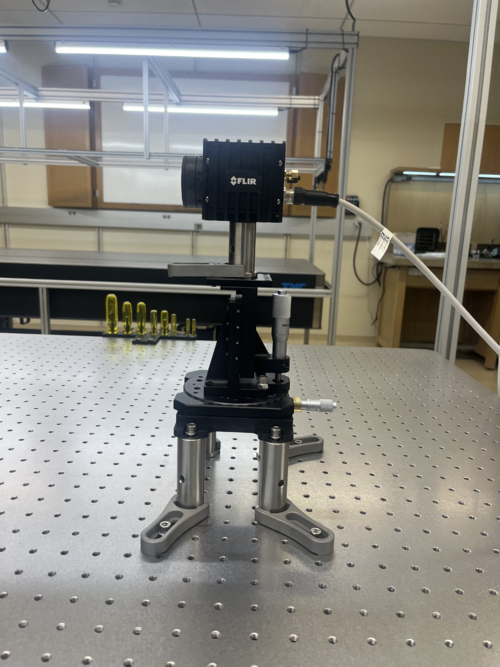
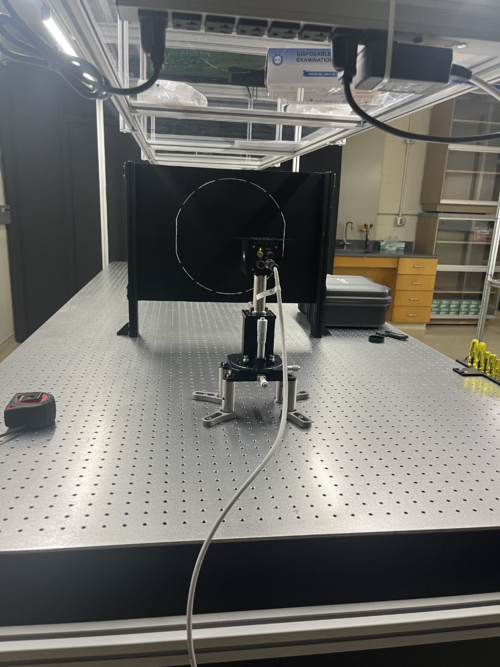
Camera Stage Setup
Once the screen was in place, the camera stage was set up by placing the XY-Translational with Rotation stage on four 3" optical posts. Then, the z-axis stage was placed in the center of that, with another 3" optical post on top, which was then topped with the camera. This was set and clamped down ~22.5" from the screen. This was about 1" closer than expected based on our theoretical models.
Fine Alignment
We used the visible camera to fine align the screen and to test the setup. Notably, the visible camera is placed below the infrared and thus requires a calibration in order to ensure the two are aligned on the computer image. This can be set by hand using the FLIR proprietary software (FLIR CamWeb) and adjusting the "MSX alignment". The image mode "Thermal MSX" allows both the visible and IR camera to be displayed at once and the difference in their positioning can be seen. We found an offset of ~0.5m to be nearly accurate (note: using this method, although you can get more accurate than this, the displayed value only has one significant figure).
In order to align the camera, we first used the exposed top edge to judge whether the camera was appropriately centered on the screen. We set the rotation as close as possible to being in line by eye, then adjusted the y-axis until the gap on both corners was a similar size, thus indicating that the rotation and y-position were correctly set. Rotationally, the camera required only a refinement of -1/2 degree. The y-axis is set at 1.25. Then, the camera was pulled as far from the screen as possible using the x-axis to allow the screen to be easily centered using the z-axis. Once the outlined test mass was centered, the x-axis was used to bring the camera close until the screen just barely filled the field of view. The x-axis is at 2.25. The z axis is set to it full dynamic range at 10. Unfortunately, the camera is still slightly too tall for the screen, likely requiring the purchase of a new optical post about 0.5in shorter the current one. This interchange will likely require a new fine alignment after.
Basic Imaging Tests
The camera was also focused on the screen based on the manufacturer's printed distance on the camera itself (using 22.5", or 0.572 m). Using the FLIR proprietary software, the camera appears to be in focus in IR (a hand was used as a good focusing tool for this). Additionally, the camera does pick up heat on the other side of the screen. A hand can be lightly seen warming the screen, as can a soldering iron tip. This was a very imprecise visual tool, but does indicate that the camera and screen are working roughly as expected.
Next Steps
A new optical post that is ~2.5" tall should be ordered to replace the one under the camera currently. The heating system also needs to be ordered and set up. Currently we are debating between a parabolic reflector with a hole in the back, and one without, as each would require a different mounting mechanism for the cartridge heater. |
| Attachment 1: IMG_6751.png
|
|
| Attachment 2: IMG_1146.png
|
|
| Attachment 3: IMG_6756.png
|
|
|
5
|
Mon Jun 6 17:11:48 2022 |
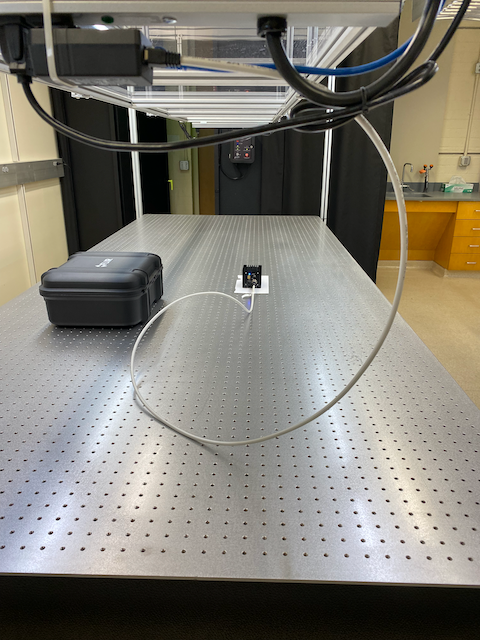
Jon | Update | Cameras | FLIR Camera Setup |
Today I tested the Spinnaker/PySpin software installations (detailed in ELOG #4) with the FLIR camera connected to chimay. It works!
Example codes
I was able to run several of the PySpin example codes. In particular, there is one which connects to the camera and streams live data to a pop-up Matplotlib window that looks very useful. It is called AcquireAndDisplay.py.
When running these, it is important to keep in mind that PySpin requires Python 3.8, which is not the default system version on chimay. So to run AcquireAndDisplay.py, for example, you must explicitly call the correct version of Python:
$ python3.8 AcquireAndDisplay.py
The standard python and python3 aliases are still linked to the system version (3.9), so calling these will result in a PySpin import error.
Git repository
I have set up a git repo for our FLIR camera control code. I have populated it with an Examples directory which contains the PySpin Reference Manual as well as all the example codes (see the README). There is a local copy of this repo on chimay at /home/controls/FLIR.
Other FLIR streaming software
In addition to the PySpin demos, there are several fully developed applications provided by FLIR. While we do not plan to use these long term, they may be very useful for debugging and cross-validation of our Python interface during development:
- Browser interface: From any web browser on the local lab network, navigate to http://192.168.1.6 and log in (credentials here). This interface supports live data streaming as well as full control of the camera settings.
- SpinView: A standalone application provided as part of the Spinnaker SDK. It supports streaming live camera data as well as saving images and videos. It can be launched from the terminal on chimay via the command: $
spinview
- Research Studio: This is FLIR's proprietary software, for which we have a one-year license. It can be launched from the terminal on chimay via the command:
$ FLIRResearchStudio
Permanent cabling
Since everything appears to be working, I ran a permanent Cat 6 cable from the lab switch to the camera's power+I/O adapter. The adapter is plugged into a UPS-protected power strip overhanging the optical table, as pictured below. To prevent the adapter from unplugging itself under its own weight, I attached a zip tie around the adapter to hold it securely in place. |
| Attachment 1: IMG_1480.png
|

|
| Attachment 2: IMG_1481.png
|
|
|
4
|
Fri Jun 3 13:03:33 2022 |
Jon | Update | Cameras | FLIR Camera Setup |
Summary
I have installed the requisite software on chimay for interfacing the FLIR A70 camera in Python. There are two packages required from FLIR:
- Spinnaker SDK, which provides the low-level camera drivers and a C/C++ API.
- PySpin, a wrapper of the Spinnaker library which provides the Python API.
These installations did not work out-of-the-box for Debian 11 (only Ubuntu is officially supported). I had to make several modifications which are documented below for future reference.
This setup has not yet been tested with the camera connected to chimay.
Documentation and Demo Codes
The PySpin package comes with a number of Python demo codes and a complete API reference. These can be found on chimay at the following locations.
- Example codes:
/opt/spinnaker/python/Examples/Python3/
- Python API reference manual:
/opt/spinnaker/python/docs/PySpinDoc.pdf
Installing Spinnaker SDK
Below were the steps required to install Spinnaker on chimay (Debian 11).
- Download the Spinnaker binaries (AMD64 architecture) and copy the tarball to, e.g.,
/home/controls on chimay.
- Unpack the tarball contents and enter the new directory:
$ tar -xf spinnaker-2.6.0.160-Ubuntu20.04-amd64-pkg.tar.gz
$ cd spinnaker-2.6.0.160-amd64
$ sudo apt-get install libavcodec58 libavformat58 \
libswscale5 libswresample3 libavutil56 libusb-1.0-0 \
libpcre2-16-0 libdouble-conversion3 libxcb-xinput0 \
libxcb-xinerama0
qt5-default, which is obsolete in Debian and no longer available via the package manager (that is, its functionality was absorbed into other Qt packages). I was able to find a workaround based on these instructions.
- Install all the dependencies of
qt5-default:
$ sudo apt-get install qtbase5-dev qtchooser qt5-qmake qtbase5-dev-tools
- Manually remove the
qt5-default dependency from the Spinnaker package.
Unpack the spinview-qt_2.6.0.160_amd64.deb package:
$ mkdir tmp
$ cd tmp
$ ar -x ../spinview-qt_2.6.0.160_amd64.deb
$ tar xf control.tar.xz
Open the file control in a text editor and delete the qt5-default dependency from the Depends list.
Then repackage the contents:
$ tar cfJ control.tar.xz control
$ ar rcs ../spinview-qt_2.6.0.160_amd64.deb debian-binary control.tar.xz data.tar.xz
$ cd ..
$ rm -rf tmp
qt5-default dependency.
- Now proceed with running the install script:
$ sudo sh install_spinnaker.sh
This will install the Spinnaker library at /opt/spinnaker. Spinnaker also provides a standalone GUI application, SpinView, which can be executed from the terminal (from any directory) via the command spinview.
Installing PySpin
The main challenge with installing PySpin was that it is currently only supported for Python <=3.8. The system installation on Debian 11 is Python 3.9 and 3.8 is not available within the package manager. Following these instructions, I manually installed a second version of Python (3.8) on chimay, in a way that should not interfere with the system installation.
The Python 3.8 executable is in the system path and can be run only via the command python3.8. It is not symlinked to python or to python3. Those remain linked to the preexisting Python 3.9.
After installing Python 3.8, I proceeded with the installation as follows:
- Download the PySpin package (x86_64 architecture) and copy the tarball to, e.g.,
/home/controls on chimay.
- Unpack the tarball contents and into a new directory:
$ mkdir python
$ mv spinnaker_python-2.6.0.160-Ubuntu20.04-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.tar.gz python
$ tar xf spinnaker_python-2.6.0.160-Ubuntu20.04-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.tar.gz
- Move the new directory into the Spinnaker installation directory:
$ sudo mv python /opt/spinnaker
$ cd /opt/spinnaker/python
- Install the dependencies:
$ sudo python3.8 -m pip install --upgrade numpy matplotlib
- Finally, install PySpin itself:
$ sudo python3.8 -m pip install spinnaker_python-2.6.0.160-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
If this succeeded, you should now be able to enter import the package PySpin as
$ python3.8
>>> import PySpin
without error. |
|
3
|
Thu Jun 2 21:55:02 2022 |
Jon | Update | Cameras | FLIR Camera Setup |
The new FLIR A70 infrared camera has arrived. Tyler and I unpacked it in the lab yesterday. In less than an hour, we succeeded in powering it on and connecting it to the lab network. We have assigned it the static IP address 192.168.1.6.
Online Configuration Portal
The FLIR camera can be configured, as well as stream live data, through a web browser interface. It can be accessed from any workstation on the lab network by navigating in the browser to http://192.168.1.6. The login credentials are stored here (log in with your LIGO.ORG credentials).
Next Steps
The next step is to install FLIR's Python API for controlling and reading out the camera on chimay. The API comes with demo codes which we can use to test the basic connectivity and which will serve as a reference for developing our own Python interface over the summer. |
| Attachment 1: IMG_1473.png
|

|
| Attachment 2: IMG_1474.png
|

|
|
2
|
Thu Jun 2 16:14:58 2022 |
Jon | HowTo | General | Custom conda environment on JupyterHub |
Cross-linking instructions: How to run a Jupyter notebook in your custom Conda environment |
|
1
|
Sun Apr 10 15:39:49 2022 |
Rutuja Gurav | HowTo | Computer Scripts/Programs | HowTo: Renew the Let's Encrypt SSL certificate using certbot |
Port 80 is kept closed by default. This might be causing the certbot auto-renewal cronjob to fail. Therefore we must renew the certificate manually.
Step 1: Open port 80. (This is needed as the certificate renewal process runs some tests which requires client communication over port 80)
Step 2: Run the following command
sudo certbot certonly --force-renew -d richardsonlab.ucr.edu
Step 3: Confirm the certificate was renewed by running the following command
sudo certbot certificates
|